
Autotrophs are plants that can use energy from light to synthesis, or create, their own nourishment. Many people feel they are “feeding” a plant when they plant it in soil, water it, or set it in direct sunlight, however none of these actions are considered nourishment. Rather than that, plants create glucose from sunshine, water, and the gases in the air. Glucose is a type of sugar that plants require to exist. Photosynthesis is a process that occurs in all plants, algae, and even certain microbes. Plants require three elements to perform photosynthesis: carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight.
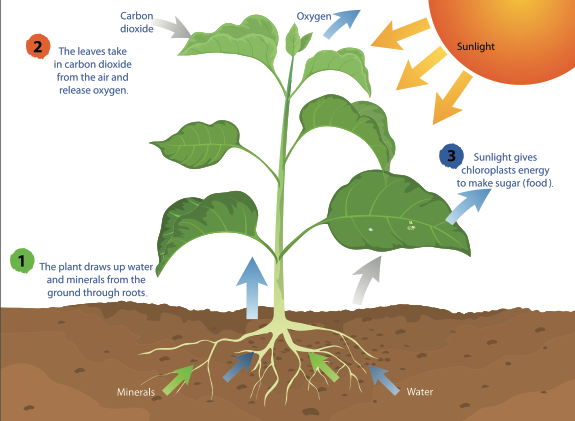
Plants, like humans, require gas intake to survive. Animals breathe in gases via a process known as respiration. Animals inhale all of the gases in the atmosphere during the respiration process, but the only gas that is held and not immediately expelled is oxygen. Photosynthesis, on the other hand, occurs when plants take in and utilise carbon dioxide gas. Carbon dioxide penetrates a plant’s leaves, blossoms, branches, stems, and roots through minute holes. Additionally, plants require water to produce food. Water availability varies according on the environment in which a plant grows. For instance, desert plants, such as cactus, have less available water than a lilypad in a pond, but every photosynthetic creature has some type of adaption, or specific structure, for collecting water. The roots of the majority of plants are responsible for water absorption.
The final requirement for photosynthesis is critical because it supplies the energy required to produce sugar. How can a plant synthesise food molecules from carbon dioxide and water molecules? Sun! The energy from the sun initiates a chemical reaction that degrades the carbon dioxide and water molecules and reorganizes them to form sugar (glucose) and oxygen gas. Following the production of sugar, the mitochondria convert it to energy that can be used for growth and repair. The oxygen created is expelled through the same microscopic openings that allowed the carbon dioxide to enter. Even the oxygen that is released has a secondary function. Other organisms, including animals, require oxygen to survive.
Related: The Homo Sapiens
If we were to develop a photosynthesis formula, it might look something like this:
C6H12O6 (sugar) + 6O2 = 6CO2 + 6H2O + Light energy
Photosynthesis as a whole is a process of energy transmission from the Sun to a plant. Each sugar molecule contains a little amount of solar energy, which the plant can either consume immediately or store for later use.
Consider the pea plant. If the pea plant is producing new pods, it requires a significant amount of sugar energy to grow. This is similar to how you consume food to increase your height and strength. However, rather than going to the shop and purchasing groceries, the pea plant will acquire energy from the sun in order to develop sugar. When the pea pods reach maturity, the plant may require less sugar and will store it in the cells. A hungry rabbit comes along and decides to consume some of the plant’s energy, which enables the rabbit to jump back to its home. Where did the rabbit obtain its energy? Consider the photosynthesis process. The pea pod utilised the energy from the sun to make the sugar molecules with the assistance of carbon dioxide and water. When the rabbit ate the pea pod, it ingested energy from the sun that was stored in the plant’s sugar molecules.

Humans, other animals, fungus, and other microbes are not autotrophs and so rely on sunlight. Plants create sugars through the transmission of energy from the Sun to them, which humans consume to power our everyday activities. Even when we eat chicken or fish, we are transferring energy from the Sun to our body because one organism consumed a photosynthetic organism at some point (e.g., the fish ate algae). Therefore, the next time you go for a snack to refuel your energy, give thanks to the Sun!



